How secure storage works
Let's consider a concrete example of CVS integration. When you specify a password for a CVS connection,
the application offers you an option to save your user name and password using secure storage.
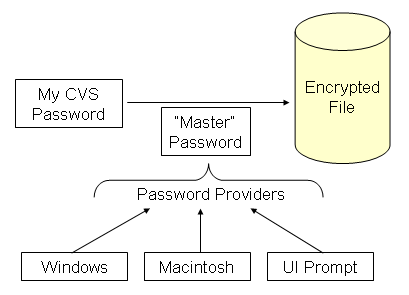
Picture 1. How secure storage works.
Your CVS password is passed as data to secure storage. Secure storage uses a "master" password
to encrypt it and store the encrypted CVS password in a file on disk.
The master password is obtained from a password provider module. The master passwords
are obtained in a "lazy" fashion, only when they are about to be used. Password providers can use
different techniques:
- on Windows, the master password is generated as a random value that is encrypted based on your
Windows login information and stored in secure storage;
- on Macintosh, the master password is initially created as a random value that is stored in
the OS keyring;
- the default password provider simply prompts you for a password;
- other password providers might be supplied in your application.
When data is saved with secure storage, the password provider is selected based on the priorities from
the list of enabled password providers. Only that provider can be used in future to decrypt the data.
Secure storage
Password recovery
Life of a master password
Secure storage preference page
Secure storage runtime options
