Keys
The function of the keyboard can be extensively customized in Eclipse using the
General > Keys
preference page. Within Eclipse, key strokes and key sequences are assigned to
invoke particular commands.
Key Strokes, Key Sequences, and Key Bindings
A 'key stroke' is the pressing of a key on the keyboard, while optionally holding down one
or more of these modifier keys: Ctrl, Alt (Option on the Macintosh), Shift, or
Command (only on the Macintosh.) For example, holding down Ctrl then
pressing A produces the key stroke Ctrl+A. The pressing of the modifier keys themselves
do not constitute key strokes.
A 'key sequence' is one or more key strokes. Traditionally, Emacs assigned two or three key stroke key sequences to particular
commands. For example, the normal key sequence assigned to Close All in emacs is Ctrl+X Ctrl+C.
To enter this key sequence, one presses the key stroke Ctrl+X followed by the key stroke Ctrl+C.
While Eclipse supports key sequences of arbitrary lengths, it is recommended
that keyboard shortcuts be four key strokes in length (or less).
A 'key binding' is the assignment of a key sequence to a command.
Schemes
A 'scheme' is a set of bindings. Eclipse includes two schemes:
- Default
- Emacs (extends Default)
The Default scheme contains a general set of bindings, in many cases recognizable
as traditional key sequences for well known commands. For instance, Ctrl+A
is assigned to Select All, and Ctrl+S is assigned to Save.
The Emacs scheme contains a set of key bindings familiar to users of Emacs.
For instance, Ctrl+X H is assigned to Select All, and Ctrl+X S is assigned to Save.
It is important to understand why the Emacs scheme says that it 'extends Default'. The Emacs scheme
is not a complete set of bindings like the Default scheme. Rather, it borrows from the Default
scheme where possible, only defining explicit Emacs-style bindings where they vary from the
Default scheme. Generally, only well known commands like Select All, Save, etc. have specific Emacs key sequences associated with them.
Choose the scheme you are most comfortable with by changing the 'Scheme' setting on the
keys preference page. If you choose the Default scheme, all Emacs bindings are ignored. If you choose
the Emacs scheme, explicit Emacs-style key sequence assignments take precedence over any conflicting assignments in the Default scheme.
Contexts
Key bindings can vary based on the current context of Eclipse.
Sometimes the active part might be a Java file editor, for instance, where
a different set of key sequence assignments may be more appropriate than if
the active part was an html file editor. As a specific example, typically Ctrl+B
is assigned to Build in a context such as Java file editing, while
Ctrl+B is assigned to Make Text Bold in a context
such as HTML file editing. This context is usually determined by the active
part, but it can be influenced by the active window or dialog as well. If the
active part does not choose a particular context, the workbench will set the
active context to In Windows.
Eclipse includes a number of different contexts. Some examples are:
- In Dialogs and Windows
- In Windows (extends In Dialogs and Windows)
- In Dialogs (extends In Dialogs and Windows)
- Editing Text (extends In Windows)
- Editing Java Source (extends Editing Text)
- Debugging (extends In Windows)
- Debugging Java (extends Debugging)
- In Console
- Editing Ant buildfiles
Much like configurations, contexts can extend other contexts. For example,
the Editing Java Source context borrows key bindings from the Editing Text
context, which in turn borrows key bindings from the In Windows context.
Note: It is not recommended to promote a key binding to a context which it
extends. For example, it is not recommended to move an Editing Text key
binding to the In Dialogs and Windows context. This may have unexpected
results.
It is possible for some key bindings to work in dialogs. Those key bindings
are assigned to the In Dialogs and Windows context. One example of such a
key binding is the key binding for "cut". It is possible to change these key
bindings. For example, it is possible to have Ctrl+X as cut in dialogs, but
Ctrl+W as cut in windows.
Platform and Locale
Key bindings also vary by platform and locale. On the Macintosh platform, Command+S is assigned to Save, instead of the usual Ctrl+S. On Chinese locales (zh), Alt+/ is assigned to Content Assist, instead of the usual Ctrl+Space.
The current platform and locale is determined when Eclipse starts, and does not vary over the course of an Eclipse instance.
Customizing Key bindings
With multi-stroke key sequences, schemes, and contexts, there are a
lot of things to keep in mind when customizing key bindings. To make things
easier, all key customization is done on the
General > Keys
preference page.
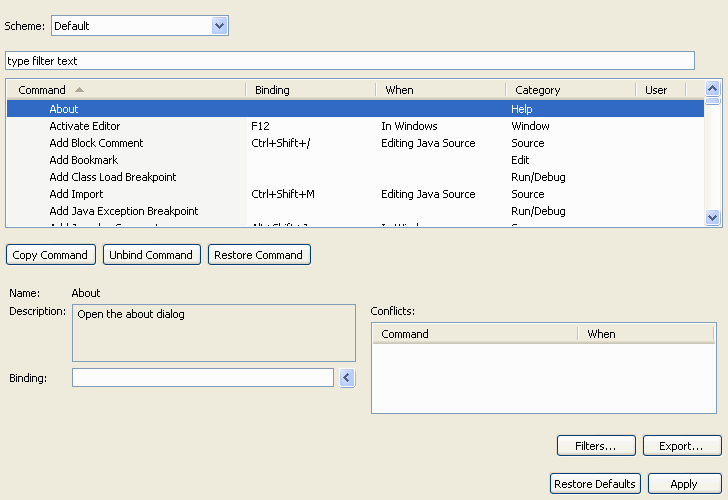
In this example we want to bind CTRL+5 to the About command. By default
the keys preference page will show you all possible keybindings. You can see
the About command listed in the Help category. You can bind the command
by putting focus in the Binding text box and pressing CTRL and 5 like you
would if you were executing the command.
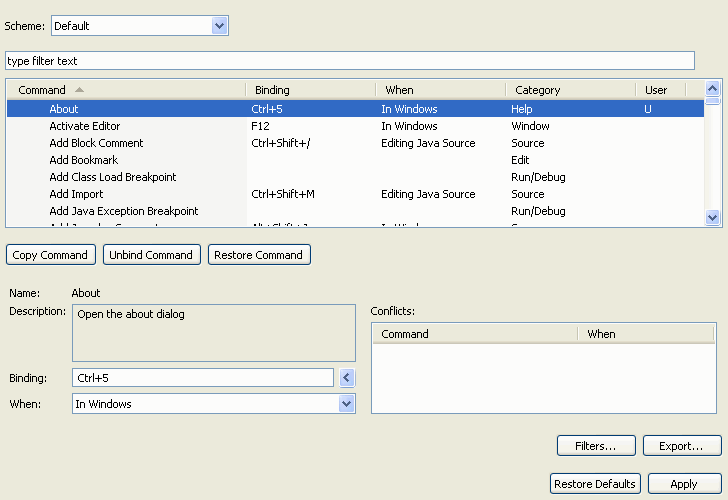
When you type CTRL+5 you have created a binding for About. The right-most column
will indicate that this is a user binding by displaying a U. If there was
a conflict with another key, this column would also display a C. The binding
will be in the default context, "In Windows". You can now
use the When combo box to change the key binding context (for example, to move
this binding to "Editing Text").
If you wanted to add a second key binding to About, you can use the
Copy Command button to create a second command entry for you to bind
another key to. If you want to delete a binding, you can either use the
Remove Binding button or simply give focus to the Binding text box
and hit Backspace.
The Dynamic Nature of Key bindings
Key bindings are provided by plug-ins, and in Eclipse, plug-ins can be added or removed.
This can cause key bindings declared by these plug-ins to be added or removed.
Eclipse stores custom key bindings in a way to compensate for this.
Consider the example above where CTRL+6 was assigned
to About in the Default scheme. Say you install a new
plug-in that assigns CTRL+6 to a particular
command. Eclipse will preserve your assignment to About.
Conflict Resolution
There are only a finite number of simple, common key strokes available to
assign to a multitude of commands. We have seen that scheme, context,
platform, and locale all partition key sequence assignments into domains where
they don't conflict with one another. Consider the case for Ctrl+B
above if contexts did not exist. One plug-in would assign Ctrl+B
to Build, the other plug-in would assign Ctrl+B to
Make Bold Text. How would Eclipse properly resolve this conflict?
Though conflicts are drastically reduced by employing the above mechanisms,
they can still occur. Two plug-ins, independent of one another, could assign
the same key sequence to different commands with the same context, scheme,
platform, and locale. Consider if a plug-in assigned Ctrl+F4 in
the In Windows context and Default scheme to one of its
commands. This directly conflicts with Eclipse assigning Ctrl+F4
to the close command in the same context and scheme.
This is a conflict. It wouldn't be proper to invoke both commands, nor would it be proper to simply choose one of the two commands to receive the key stroke.
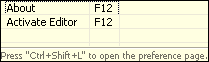
We pop up the Key Assist Dialog with the conflicting commands and allow the user
to select one. The Key Assist Dialog is the same dialog that displays
command choices for multiple key stroke key bindings. For example, if 2 commands
were bound to F12 you might see:
If the user sets a keybinding and creates a conflict, the conflicting bindings
will be displayed in the conflicts list. This can be used to navigate between
conflicting keybindings so that they can be changed.
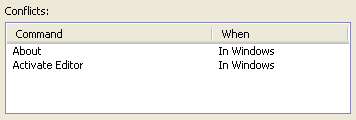
These types of conflicts can be resolved by explicitly assigning
the key sequence to one of the commands, or remove it from the other.
Another type of conflict can be caused by multiple-key stroke key sequences. For example, in the Emacs scheme, there are many multiple-key stroke key sequences beginning with the key stroke Ctrl+X. Ctrl+X K is assigned to Close. Ctrl+X H is assigned to Select All.
As previously mentioned, the Emacs scheme borrows key bindings from the Default scheme. In the default scheme, Ctrl+X is assigned to Cut. Though the Emacs scheme doesn't explicitly redefine Ctrl+X, pressing Ctrl+X is required as part of many of its key bindings. In the Emacs scheme, when one presses Ctrl+X, one is half way to entering one of many possible assigned key sequences. One would not expect the Cut action to be invoked at this time.
For this type of conflict, the rule is that the Ctrl+X key sequence assigned to Cut would be ignored. Otherwise, it would not be possible to complete many of the key bindings in the Emacs configuration.
Accessibility features in Eclipse
Changing the key bindings
Help
Font and color settings in Eclipse
