Editors
Most perspectives in the Workbench are comprised of an editor area and one or more
views.
You can associate different editors with different
types of files. For example, when you open a file for editing by double-clicking
it in one of the navigation views, the associated editor opens in the Workbench.
If there is no
associated editor for a resource, the Workbench attempts to launch an external
editor outside the Workbench. (On Windows, the Workbench will first
attempt to launch the editor in place as an OLE document. This type
of editor is referred to as an embedded editor. For example, if you have a
.doc file in the Workbench and Microsoft Word is registered as the editor for .doc
files in your operating system, then opening the file will launch Word as an OLE document within the Workbench editor
area. The Workbench menu bar and toolbar will be updated with options for
Microsoft Word.)
Any number of editors can be open at once, but only
one can be active at a time. The main menu bar and toolbar for the
Workbench window contain operations that are applicable to the active
editor.
Tabs in the editor area indicate the names of
resources that are currently open for editing. An asterisk (*) indicates that an editor has unsaved
changes.
By default, editors are stacked in the editor area,
but you can choose to tile them in order to view source files simultaneously.
Here is an example of a text editor in the Workbench:
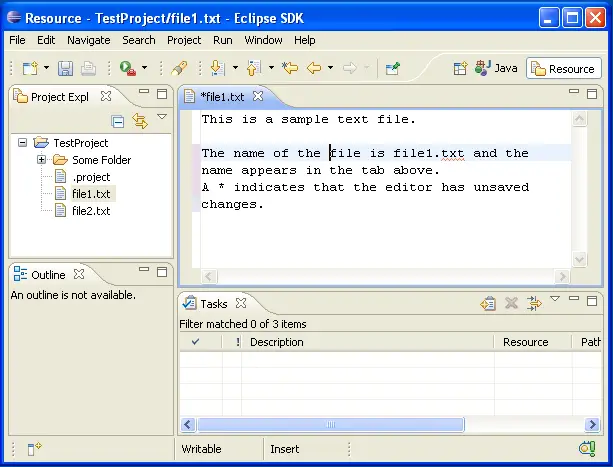
The gray border at the left margin of the editor area may contain
icons that flag errors, warnings, or problems detected by the system. Icons also
appear if you have created bookmarks, added breakpoints for debugging, or
recorded notes in the Tasks view. You can view details for any icons in the left
margin of the editor by moving the mouse cursor over them.
Workbench
External editors
Bookmarks
Tasks view
Project Explorer view

Opening files for editing
Associating editors with file types
Editing files outside the Workbench
