Marker help and resolution
In
Resource markers, we saw how plug-ins can
define specialized marker types in order to annotate resources with
information. The
readmetool example defines its own markers in order to demonstrate two
marker-related workbench extensions: marker help and marker
resolutions. The marker definition is in the readme plug-in's manifest
markup:
<extension id="readmemarker" point="org.eclipse.core.resources.markers" name="%ReadmeMarker.name">
<super type="org.eclipse.core.resources.taskmarker"/>
<super type="org.eclipse.core.resources.textmarker"/>
<persistent value="true"/>
<attribute name="org.eclipse.ui.examples.readmetool.id"/>
<attribute name="org.eclipse.ui.examples.readmetool.level"/>
<attribute name="org.eclipse.ui.examples.readmetool.department"/>
<attribute name="org.eclipse.ui.examples.readmetool.code"/>
<attribute name="org.eclipse.ui.examples.readmetool.language"/>
</extension>
The tool defines a marker that inherits from the platform's text marker and
task marker. It also defines named attributes for the marker.
Marker attributes can be set and queried.
Since the new readme marker is a kind of text marker, it
inherits the text marker attributes. The text marker attributes include
the character location of the marker.
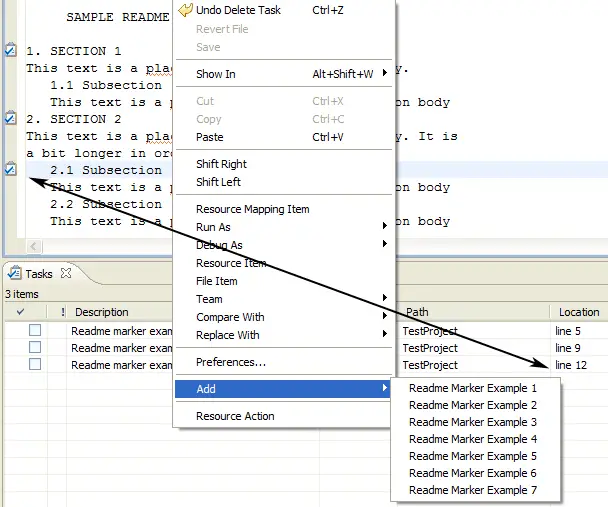
Markers can be added to a .readme file using the readme editor's popup
menu. (The popup menu actions are added dynamically in ReadmeTextEditor.editorContextMenuAboutToShow(IMenuManager
parentMenu)). Once added,
the markers appear on the left side of the editor and in the tasks view.