Out of the box, the EMF Validation Framework provides support for defining constraints in
two languages: Java and OCL. Clients can plug in additional languages by providing
constraint parsers on the
org.eclipse.emf.validation.constraintParsers
extension point. Extension associate an implementation of the
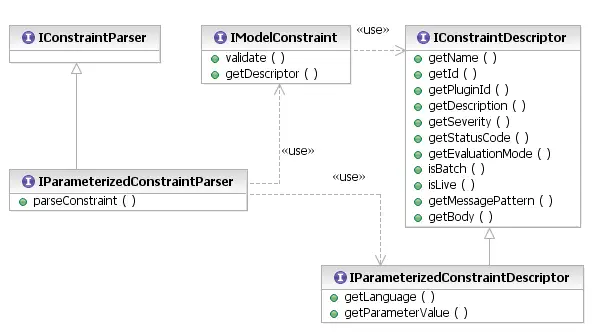
IConstraintParser
interface with an unique language name.
[
as SVG]
The IConstraintParser interface exists to unify the deprecated
IXmlConstraintParser and new
IParameterizedConstraintParser
interfaces. A constraint parser accepts an
IParameterizedConstraintDescriptor
bearing its language and parameters which a
constraint provider will supply according to what the
language requires. If the descriptor supplied by a constraint provider does not have all of
the parameters required by the constraint parser, it should throw a
ConstraintParserException.
The following example is the framework's OCL constraint parser, from the
org.eclipse.emf.validation.ocl plug-in:
public IModelConstraint parseConstraint(IParameterizedConstraintDescriptor desc) {
return new EcoreOCLConstraint(desc);
}
public class OCLConstraintParser implements IParameterizedConstraintParser {
public IModelConstraint parseConstraint(IParameterizedConstraintDescriptor desc) {
return new EcoreOCLConstraint(desc);
}
private static class EcoreOCLConstraint
extends AbstractOCLModelConstraint<EClassifier, Constraint, EClass, EObject> {
EcoreOCLConstraint(IConstraintDescriptor descriptor) {
super(descriptor);
}
@Override
protected EcoreEnvironmentFactory createOCLEnvironmentFactory() {
return EcoreEnvironmentFactory.INSTANCE;
}
}
}
The
AbstractOCLModelConstraint
class obtains an OCL expression from the body attribute of the
constraint descriptor and parses it in the context of the EClass(es)
that the constraint targets. The framework's implementation assumes a basic Ecore environment.
Clients may define their own variants of the OCL language, via constraint parsers that create
custom subclasses of the AbstractOCLModelConstraint, in order to
- use a different environment implementation (e.g., for the UML metamodel)
- introduce custom ("global") variables
- to use an OCL environment that includes additional operations and/or attributes,
themselves defined using OCL
See the
MDT OCL Programmer's Guide
for more information about working with OCL.
Copyright (c) 2000, 2007 IBM Corporation and others. All Rights Reserved.
